Practical guide to Correlation measures
TLDR
Use Kendall for most cases its the best option.
Correlation Measure
Correlation measure is used to measure the degree of relationship between two variables. There are different kinds of correlation measures that can be used depending on the type of data and use case. Some common correlation measures are Pearson, Spearman and Kendall correlation. In this post I will try to explain briefly what these do and when to use them. Formulas for these can be found easily elsewhere, Implementations are available in Pandas library.
Pearson
Can compute degree of relationship between two variables however it assumes that data is Linear and Homoscedastic.
- Linearity: X,Y are linear if, graph of X,Y is a straight line
- Homoscedasticity: X,Y are homoscedastic if they come from some Gaussian distribution.
What does that mean? Well to put it in simple practical points.
- Use when
- Data appears to have a simple linear relationship(If it has).
- Data is stationary (Mean, Variances, etc. dont change)
- Data appears to be normally distributed around a mean point with some variance.
- There are tests available to find out whether data is coming from a normal distribution.
- Don’t use when
- Data is non stationary
- Data is not linearly related
- It will give some readings if you use it for non linear, non gaussian data but those wont be reliable indicators of correlation.
Spearman Correlation
It is a more robust correlation measure as it does not assume anything about the distribution of the data. However it only looks for monotonic relationships, and is generally suited for ordinal variables. eg: Finding the relationship between the order of students who finish a race with the amount of hours they practice.
Note that this captures only the monotonic relationships, as can be seen in Fig 1 however it cannot capture non monotonically related variables as in Fig 2.
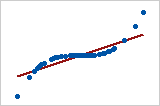
Fig 1: Spearman coeff = 1
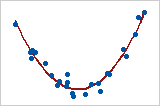
Fig 2: Spearman coeff = 0
Note: Spearman correlation is good for finding out whether two variables are independent or not, however when they are not independent it doesn’t convey much information.
- Use when
- The relationship is monotonic (either always increasing of always decreasing)
- Order of values of a variable may be of interest (Spearman rho)
Kendall Correlation
Kendall correlation does not assume anything about the distribution of the data like Spearman. Spearman has a flaw it is good to find whether there is monotonic dependence or not, if there is monotonic dependence the value is difficult to interpret. Kendall on the other hand can quantify the strength of dependence between variables.
- Advantages
- Non-parametric (Doesn’t assume distribution of the data)
- Can be used to establish whether two variables are dependent or not
- Can quantify, how much dependency is there.
References
Minitab Express Support’s page on correlations
Statisticssolutions.com’s page on Correlation
Wikipedia - Pearson Correlation
Wikipedia - Spearman Correlation
Statsdirect - Kendall Correlation
Wikipedia - Kendall Correlation